Knee replacement surgery has evolved significantly with the integration of robotic technology, offering greater precision and faster recovery times. Yet, the surgical approach, how the surgeon accesses the joint, still plays a vital role in outcomes. Two widely discussed techniques are the traditional medial parapatellar approach and the muscle-sparing subvastus approach. Let’s explore how these methods compare in the context of robotic knee arthroplasty.
Understanding Surgical Access in Knee Replacement
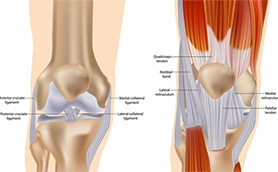
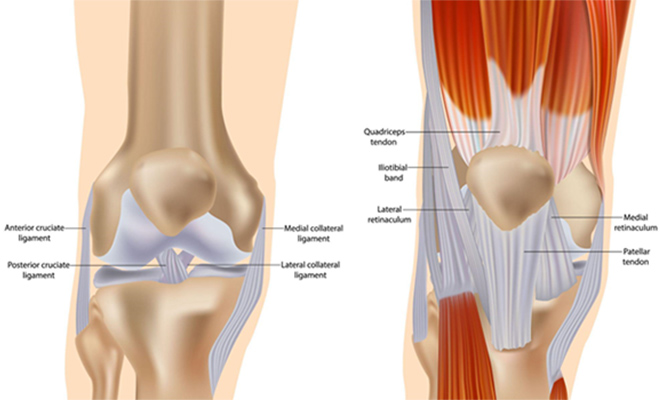
During total knee arthroplasty (TKA), the surgeon must access the joint by making an incision and moving or splitting surrounding tissues. The traditional medial parapatellar approach involves splitting the quadriceps tendon to reach the knee, allowing broad visibility and familiarity for most surgeons. By contrast, the subvastus approach navigates under the vastus medialis muscle, preserving the quadriceps tendon entirely.
While both techniques aim to restore joint function and alignment, their anatomical differences can affect muscle recovery, pain, and rehabilitation speed.
Benefits of the Subvastus Approach
The subvastus approach, often referred to as a “quadriceps-sparing” technique, has gained popularity for its potential to promote earlier mobility and less discomfort following surgery. Some notable advantages include:
- Preservation of the quadriceps tendon, reducing trauma to the extensor mechanism
- Faster initial functional recovery, including earlier ability to perform straight-leg raises
- Less post-operative pain and inflammation reported in some patients
- Improved knee stability in the early post-op period
However, this approach may be technically more demanding, especially in patients with high body mass index or limited flexibility.
Why the Traditional Approach Remains Common
Despite the advantages of the subvastus method, the traditional medial parapatellar approach remains the most widely used for a reason. It offers:
- Excellent surgical visibility, making it suitable for complex or revision cases
- Ease of exposure, especially when severe deformity or stiffness is present
- Proven long-term outcomes, backed by decades of clinical data
- When paired with robotic assistance, this method still allows for highly precise implant placement and alignment, which are crucial for joint longevity.
Robotic Technology Levels the Field
The use of robotic-assisted systems in knee arthroplasty enhances both approaches by providing real-time feedback, patient-specific planning, and accurate bone cuts. Whether using the subvastus or traditional route, robotic tools help optimize implant positioning and soft tissue balancing, key factors in overall success.
Choosing the Right Technique
The decision between the subvastus and traditional approach depends on factors such as patient anatomy, mobility, and the surgeon’s experience. An orthopedic surgeon specializing in robotic knee arthroplasty can help determine the most suitable approach based on your specific needs.
If you’re exploring surgical options for knee arthritis, consider scheduling a consultation at the Oklahoma Joint Reconstruction Institute for a personalized treatment plan supported by advanced technology and expert care.
AUTHOR: Dr. Paul Jacob is a certified master surgeon in joint replacement and robotic joint replacement of the hip and knee in Oklahoma City. Dr. Jacob is recognized as one of the Top 3 Orthopedic Surgeons in Oklahoma, who has performed over 7000 robotic joint replacement procedures. Dr. Jacob is active in numerous research studies on joint replacement technology and robotic outcomes.